Procedures
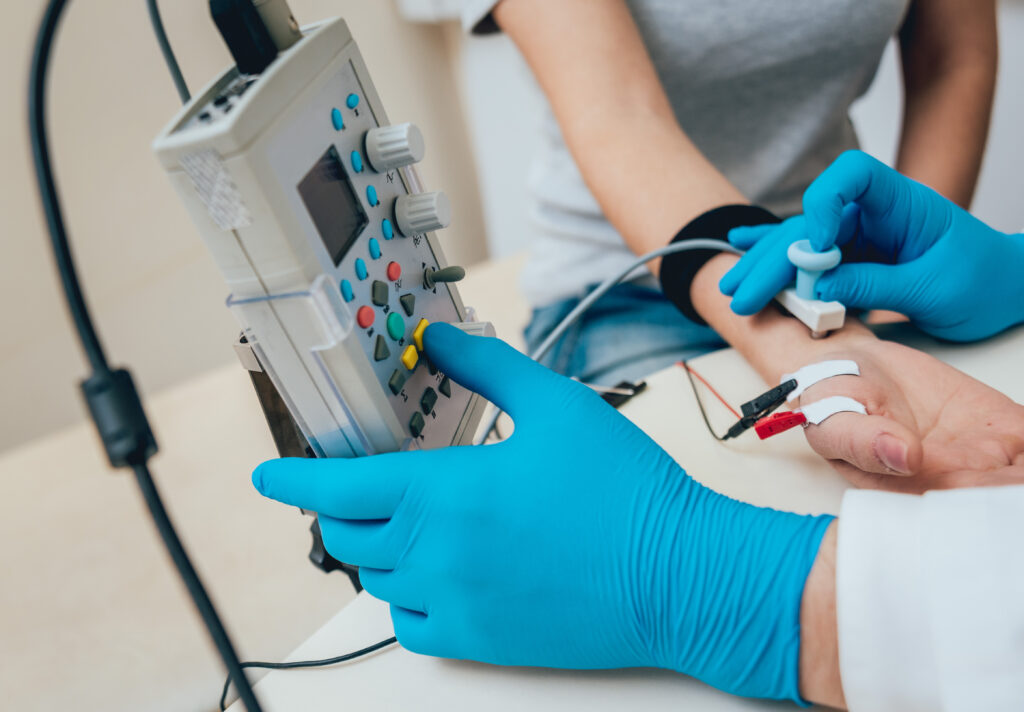
Nerve conduction study is a diagnostic test that involves electrical stimulation of peripheral nerves and an analysis of the recorded responses. Many patients describe the sensation of NCS to be like that of using a TENS machine. The readings obtained determine how quickly the electrical impulse travels through the nerve and help identify the site and degree of nerve damage. Some common indications for NCS are, carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, Guillain-Barre syndrome, traumatic nerve injuries and drop foot. No special preparation is necessary prior to NCS. It helps if loose clothing is worn and no body lotion is applied, so the electrodes attach well to the skin. Please inform us if you have a cardiac pacemaker fitted.
EMG is a test that is complementary to NCS. It is performed by inserting a fine needle into a muscle to record and analyse its electrical activity. You will be asked to relax the muscle at first, then tense it a little and finally activate it maximally. This provides extremely useful information not only about the muscle being tested but also about the nerves the control that muscle. Once again, no preparation is necessary prior to the test, apart from wearing loose clothing that makes access to the body part that needs to be tested easy. Please let us know if you are needle phobic or tend to faint easily when giving blood.
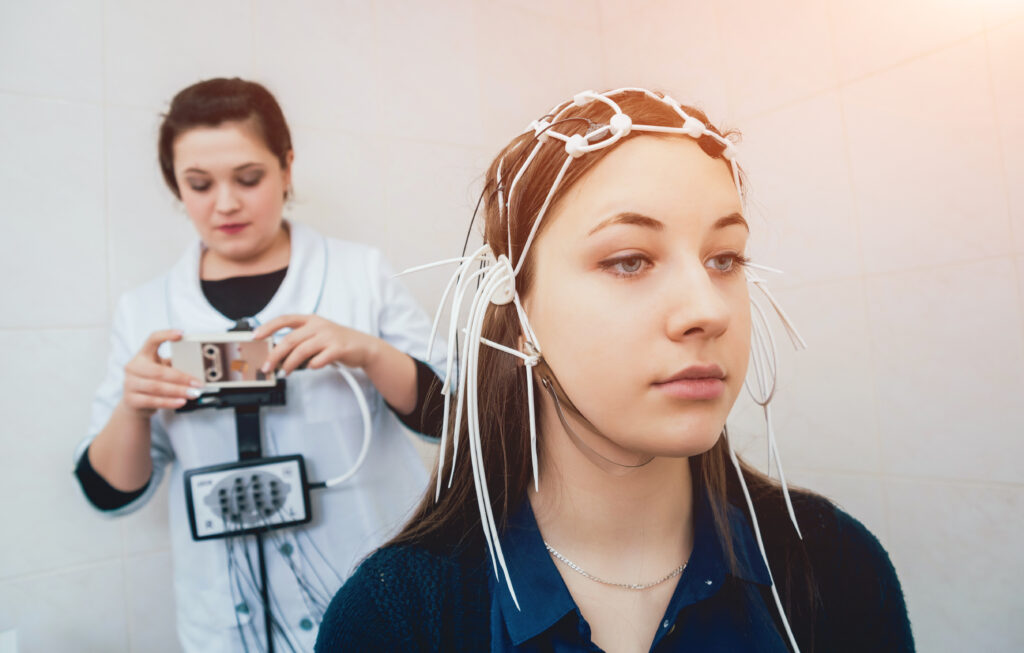

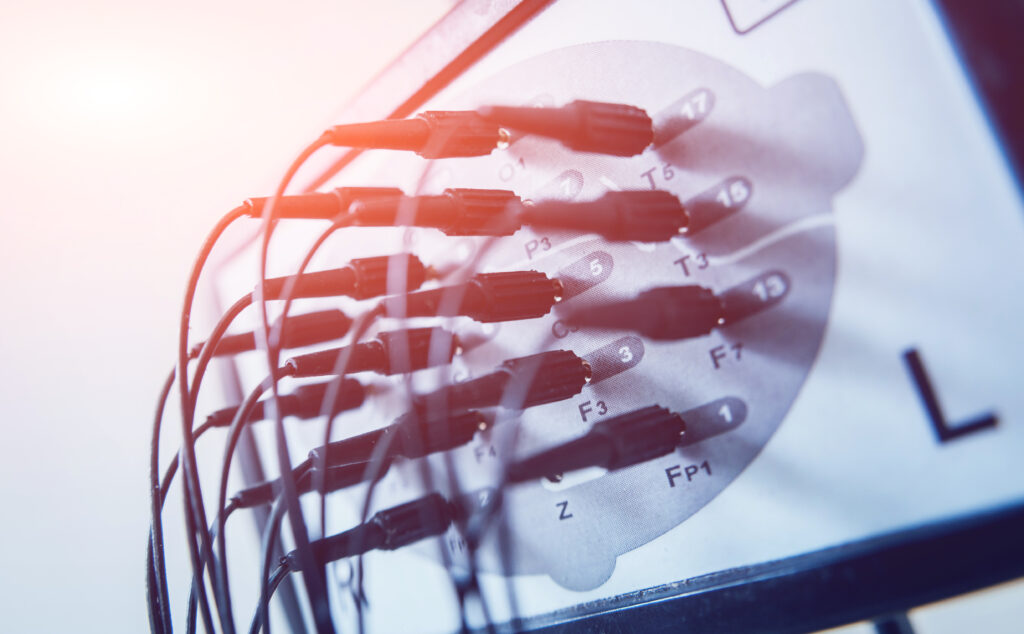
This is a real time recording of the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. A routine EEG is non-invasive and the whole process of setting up the electrodes and the recording can take around an hour. To try and “stimulate” the brain, you will be asked to look at a flashing light and be asked to breathe deeply for around 3 minutes. The EEG recording is done by a highly trained physiologist who will guide you through the entire process. I will subsequently analyse the recording and send a report to the referring doctor. An EEG can help identify the cause of symptoms such as seizures (fits) and memory loss. It can also be useful when a brain tumour or viral infection of the brain (encephalitis) is suspected. In preparation for the test, we ask that you dry you hair thoroughly and avoid using styling gel, hairspray, or oil on your hair.
Modern technology has enabled secure, remote reporting of EEG’s, ambulatory EEG’s and video-telemetry recordings. I currently provide this service for a trust and an agency. I would be happy to discuss this in further detail should it be of interest to your hospital. Report turnaround times are short, and I can attend MDT meetings to discuss my findings with the clinical team.
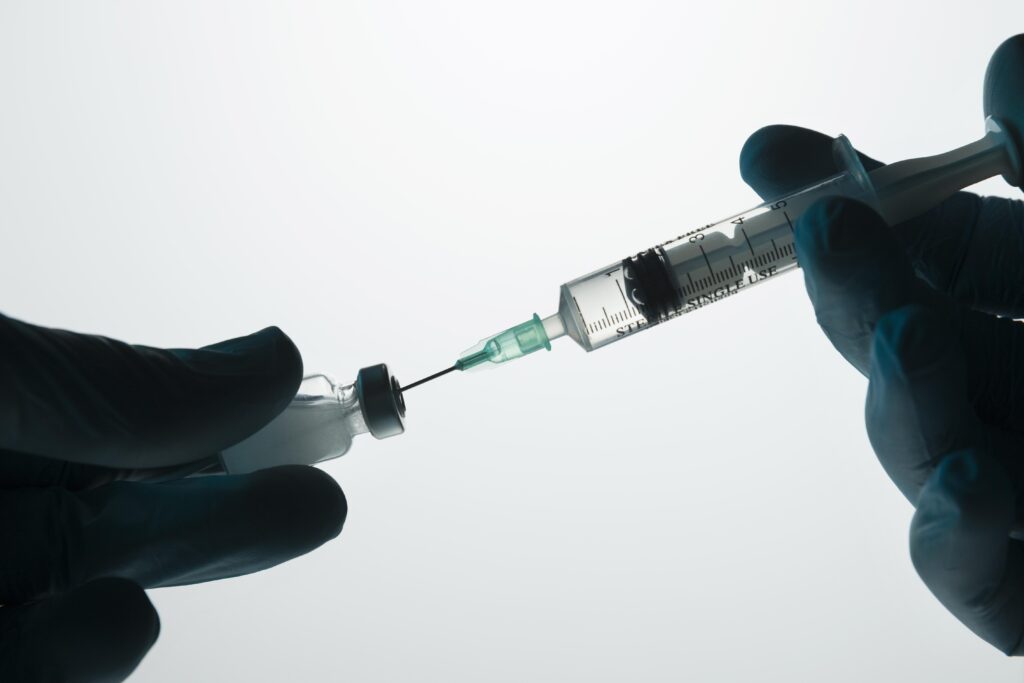
BOTOX FOR DYSTONIA
Botulinum toxin (Botox) is a chemical that is produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. When purified and administered in a small dose, this chemical reduces the excess muscle activity caused by dystonia. It acts by blocking the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine which is responsible for making muscles contract. As a result, the signals that would normally be telling your muscle to contract are stopped, the muscle spasms are reduced or in some cases may cease completely for a while. Prior to giving you the Botox injections, I will need to identify the most affected muscles by observing your abnormal postures or movements, feeling for the muscle spasm and/or by doing EMG.
It is not possible to treat generalised dystonia with Botox injections. Dystonia affecting one or two muscle groups is likely to benefit most from Botox therapy. The injections usually take a few days to have an effect and can last several weeks. Prior to having Botox therapy, please let us know if you have had a previous allergic reaction to it.
When possible I explain things in easy to understand, non-medical jargon